Ludwig Angina is a potentially life-threatening condition that demands immediate attention. While it originates in the oral cavity, its impact can extend far beyond. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the nuances of this infection, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the critical steps involved in its management.
What is Ludwig’s Angina?
Ludwig’s Angina is a relatively uncommon yet severe bacterial skin infection that specifically targets the mouth, neck, and jaw areas. Ludwig’s Angina is a rapidly spreading infection that affects the soft tissues beneath the tongue. It is classified as a type of cellulitis.
This condition is more commonly found in adults rather than children. If left untreated, the infection can cause the tongue to swell, leading to breathing difficulties or blockage as the infection spreads.
What is the cause of Ludwig’s Angina?
This skin infection is caused by bacteria that originate from dental infections or poor oral hygiene. Ludwig Angina can develop as a result of various dental conditions, such as cavities or tooth abscesses, particularly in the second and third molars. Additionally, periodontitis or gingivitis can also contribute to the development of Ludwig’s Angina.
The most common types of bacteria that cause Ludwig’s Angina are streptococcal and staphylococcal bacteria. Specifically, Streptococcus viridans, Staphylococcus epidermis, and Staphylococcus aureus are frequently associated with this condition.
What else increases Ludwig’s Angina risk?
Your susceptibility to Ludwig Angina may heighten if you possess any of the following factors:
- Fractured jawbone
- Tongue piercing
- Jawbone infection
- Mouth injury
- Abscess in the tonsils
- Infection in the salivary glands
- Thyroglossal cyst
Maintaining proper oral hygiene with the guidance of your dentist in Cincinnati is crucial for various reasons, one of which is minimizing the risk of severe conditions such as Ludwig Angina.
What are the signs and symptoms of Ludwig’s Angina?
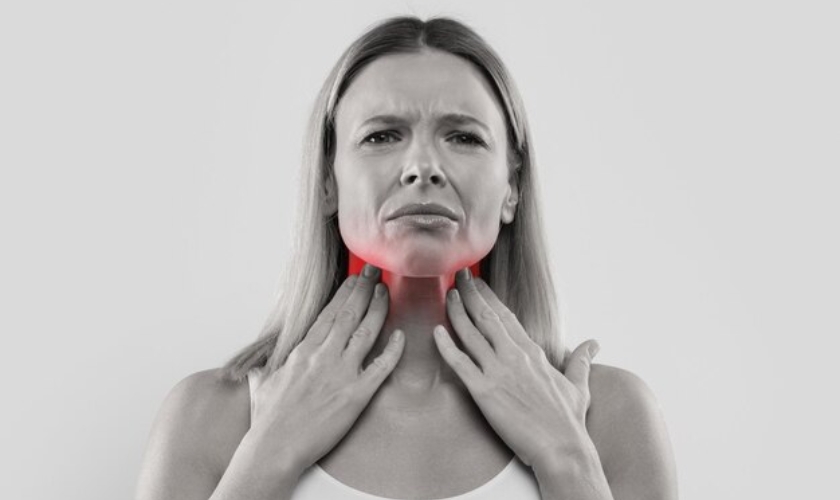
The signs and symptoms of Ludwig’s Angina often encompass fever, mouth pain, neck swelling, and a swollen tongue. Additional symptoms may include:
- Chills
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Sore throat
- Painful swallowing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Drooling
- Limited jaw opening
- Slurred speech
- Ear pain
In severe cases of Ludwig’s Angina or if left untreated, symptoms may escalate to:
- Chest pain
- Breathing difficulties or potential blockage
- Confusion and cognitive challenges
- Severe dehydration
Is it possible to prevent Ludwig’s Angina?
In the majority of cases, you can take steps to prevent this uncommon yet severe skin infection.
Good oral hygiene should be one of the first preventive measures. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing your teeth daily, as well as scheduling regular cleanings with a dentist. During your appointment, the dentist will examine your teeth for any indications of tooth decay, infection, or the accumulation of plaque.
It is advisable to steer clear of tongue piercings and other mouth piercings that may facilitate the entry of bacteria into the jawbone and soft tissues. If you are experiencing dental pain, gum bleeding, or loose teeth, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
In addition to scheduling regular dental checkups, it is important also to schedule regular doctor checkups. It is crucial to keep your doctor informed about any dental infections you have had. In order to check for any signs of lingering infection, the healthcare provider may request blood cultures and blood tests.
By providing proper care and maintaining a nutritious diet, you can minimize your chances of developing the infection.
Available treatment options for Ludwig’s Angina
Swift intervention is crucial when dealing with this fast-spreading and severe infection. The primary focus of treatment is to control the infection and secure an open airway promptly.
Ensuring proper breathing is the initial step. If breathing is partially restricted, a breathing tube may be inserted through the mouth or nose. In cases of severe breathing restriction, a tracheotomy, a surgical procedure involving the insertion of a breathing tube into the windpipe, is performed.
Ludwig’s Angina leads to significant fluid accumulation in the neck and jaw region, necessitating drainage for relief and improved breathing. Doctors conduct an incision to drain the accumulated fluid.
Intravenous (IV) antibiotics are administered to combat bacteria in the oral cavity. Following the clearance of the infection, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent symptom recurrence. This comprehensive approach aims to address Ludwig Angina and promote a successful recovery swiftly.
Ludwig’s Angina demands swift and decisive action. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and emergency management steps is crucial for both the public and healthcare professionals. By recognizing the signs early and seeking immediate medical and dental care from your dentist in Cincinnati, individuals can navigate this disease effectively, minimizing the risk of complications and safeguarding their overall health.
Please call us today for all your dental concerns to avoid any complications related to your dental health.